What are Genetically Modified Organisms?
Gene Therapies
There are multiple types of techniques to gene therapy. One way is quite simple, which involves replacing the faulty gene with a good gene by using the help of viruses or nanotechnology. Another technique for gene therapy is fixing the chromosome itself to remove any defected genes. Genes that are the ones causing the disorder can be turned “on” or “off”, and they can also be reverse-mutated so they become normal genes.
Now, how is gene therapy different from other types of therapies? Gene therapy is more of a permanent solution for treating the disorder because “switching” off the disease-causing gene is more effective than giving continuous non-genetic therapeutics for a certain disease. Gene therapy involves replacing the faulty gene, so that certain diseases don’t appear again. The route of gene therapy proves to be cheaper due to the fact that patients do not constantly have to pay for non-genetic therapies. There are two types of gene therapy:
-
Germ-line therapy is when the genetic makeup of a gene is changed in an egg or sperm cell before fertilization, or changing the genetic makeup of a blastomere when it’s first starting to divide.
-
Some advantages with germ-line gene therapy is that it’s done before an organism is born, so that means the gene is normal and stays normal in future generations. It also allows for a certain desired trait to be fully included into an organism before the gene has been activated. Some disadvantages to this are that it’s very controversial, it’s not being pursued for development, and it possesses numerous risks.
-
-
Somatic therapy, is where the genetic code of a person’s body cells is changed and this usually happens in grown organisms.
-
Some advantages to this are that it’s less controversial than germ-line therapy and there are more developments in somatic therapy. Some disadvantages with somatic therapy are that the faulty gene that gets fixed in the organism doesn’t continue on into further generations.
-
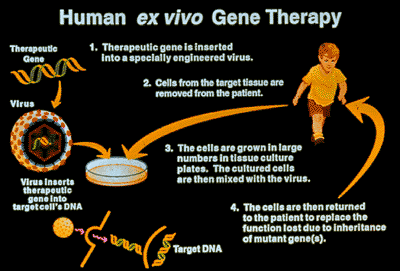
As there are different types of gene therapy, there are different ways to deliver the gene, which are ex-vivo therapy and in-vivo therapy.
-
In ex-vivo therapy, cells are first synthesized outside of an organism and then they are put in the organism to give the treatment. This method reduces the amount of risks involved with gene therapy, but it also has many limitations, such as causing immune responses or that the cell fails to work in the organism.
-
In in-vivo therapy, the gene is directly administered into the organism, through a vector or viruses. This method is used not that much as ex-vivo therapy because it holds many risks.
(Citation 19), (Citation 22), (Citation 28), (Citation 30), (Citation 31), (Citation 32), (Citation 33), (Citation 34)
What are Genes?
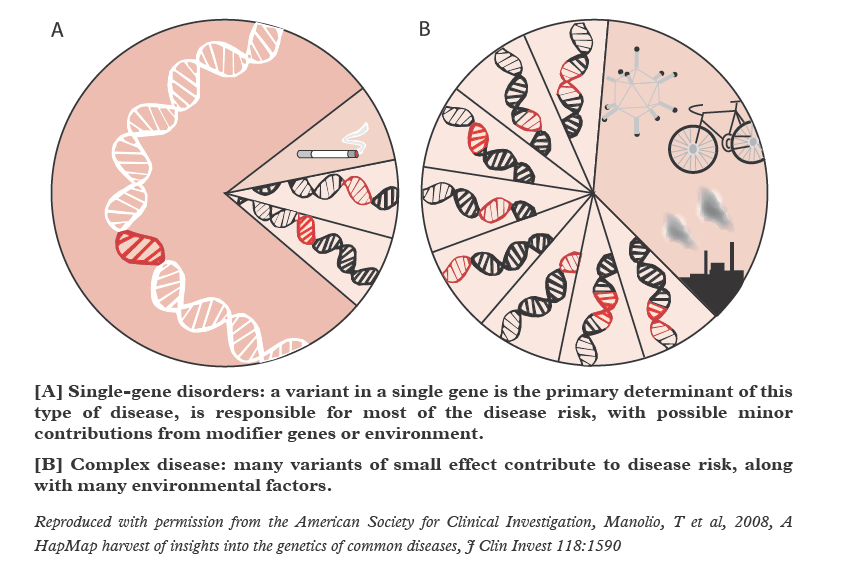
Genes are specific sequences of bases that help code to form proteins. When genes get altered so that the encoded proteins aren’t able to go about their normal functions, genetic disorders start to occur. These disorders can occur on different levels or stages. A point mutation in a gene is usually not that serious. For example, a disease that has been created by a point mutation is sickle cell anemia, which is an exception to that it’s a very dangerous disease. Genetic disorders can be classified into three levels: single gene disorders, chromosome abnormalities, and multifactorial disorders. Single gene disorders are disorders resulted when a mutation makes protein products in a single gene altered, missing or differentiated. Chromosome abnormalities are when whole chromosomes or big parts of it are missing, altered, or become duplicated. Multifactorial disorders are when mutations occur in several different genes. Genetic disorders are very harmful to many lives, but even worse is that organisms can inherit it; this means that some organisms can be carriers of certain disorders but never really experience it, and then the disease can pass on to the next generation. To treat these genetic disorders, this is where gene therapy comes to play. Gene therapy is a “way to fix a genetic problem at its source” (Citation 4), (Citation 7), (Citation 8).
Types of Genetic DIsorders
Genes are the foundation of the functions our bodies carry out on a daily basis. Genes are specific sequences of bases that code for proteins, and proteins carry out vital functions in our body. However when genes get altered, they result in deficient proteins, which cannot carry out their normal functions, and thus genetic disorders occur. These disorders can occur on different levels or stages, such as a point mutation. Point mutations can occur in three unique methods: silent mutation, missense mutation, and a nonsense mutation. While a silent mutation does not affect the structure of the protein at all, nonsense and missense mutations can drastically affect the structure of a protein, and thus alter its function. Genetic disorders can be classified into three categories: single gene disorders, chromosome abnormalities, and multifactorial disorders.
-
Single gene disorders are resulted when a mutation creates a protein with one altered gene.
-
Chromosome abnormalities result when entire chromosomes or parts of chromosomes become missing, altered, or duplicated.
-
Multifacotiral disorders are mutation in which multiple genes are altered inside a protein.Genetic disorders can evolve to become harmful to many lives, but these disorders may not occur at random, but can be inherited as well. This is where gene therapy comes into play, and is known as a “way to fix a genetic problem at its source”